CI/CD Integration with CodeScene’s Delta Analysis¶
CodeScene identifies and prioritizes technical debt, while at the same time uncovering and measuring social factors of the organization behind the system. The earlier you can react to any potential finding, the better. That’s why CodeScene offers integration points that let you incorporate the analysis results into your build pipeline.
Delta Analysis encompasses changes in the Pull Request, Merge Request, or other changeset.
The purpose of a Delta Analysis is to:
Prioritize code reviews based on the risk of the commits.
Use quality gates for the goals specified on identified hotspots inside CodeScene.
Specify quality gates that trigger in case the Code Health of a hotspot declines.
Get early warnings when new complex code is written, and detect the absence of expected changes that might indicate bugs.
In particular, it’s during the delta analysis that you identify any violations of the goals you have specified.
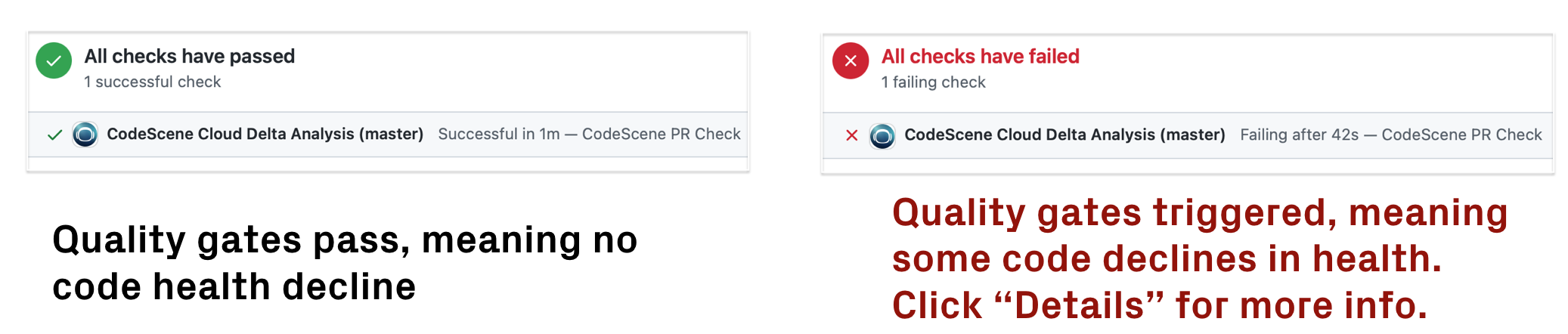
Fig. 140 CodeScene’s quality gate triggers in a GitHub check on code health decline.¶
Select a Delta Analysis Strategy¶
CodeScene has two different strategies for the delta analysis:
Full Scan: The Full Scan will supervise the code health of all files in a change set or pull request. CodeScene will always use the Full Scan for PR integrations to cover all modified content, but for delta analysis requested over the API there is a threshold; if a change set exceeeds the default limit of 50 files, then CodeScene automatically reverts to a Hotspot Scan in order to maintain quick response times. You can override this threshold via environment variables:
env variable: DELTA_ANALYSIS__LIMIT_DELTA_SCAN_TO_MAX_FILES
system property: delta.analysis_limit.delta.scan.to.max.files
Hotspot Scan: With this strategy, CodeScene limits the delta analysis to files that are identified as hotspots. This means that the most relevant modules are always checked. Non-hotspots will not be analysed for code health decline.
Integrate CodeScene in your Continuous Integration Pipeline¶
Connect automatically to external webhooks managed by CodeScene¶
CodeScene’s delta analysis can be connected to the common Git repository hosting services using webhooks or other integrations where available (e.g. GitHub Apps).
CodeScene will install webhooks at the remote service that will trigger a Delta Analysis when a pull request is created or updated. The results of the Delta Analysis will be visible on the pull request.
Delta Analysis: Use Cases and Quality Gates¶
Each time you trigger a Delta Analysis, CodeScene calculates the following information in order of importance:
Hotspot Goals: Quality Gate. CodeScene ensures that none of the goals you have specified on a hotspot (see Manage Hotspots and Technical Debt with Goals) are violated.
Code Health Decline: Quality Gate. This quality gate is triggered if any code declines in code health.
Low Code Health in New Code. This quality gate is triggered when a new module has a code health below a pre-defined threshold. This ensure that new code doesn’t start with preventable code quality issues or reckless technical debt.
Detects absent change patterns. If a cluster of files have changed together for a long time they are intimately related.This warning fires when such a temporal change pattern is broken. Please note that this may be good - we’ve refactored something - but it may also be a sign of omission and a potential bug. As a consequence, this warning is based on a self-correcting algorithm; If you keep ignoring the warning it will go away automatically as the temporal coupling decreases below the thresholds.
Positive Reinforcements. CodeScene also detects hotspots that improve their code health. This information is included as a positive reinforcement intended to show the effect of the current change set on the overall well-being of the codebase.

Fig. 141 An example on CodeScene’s quality gates where Details contain actionable feedback (example from CodeScene’s GitHub integration).¶
CodeScene’s Quality Gates focuses on Trends, not absolute values¶
You might look sceptically at automated quality gates. After all, many code analyses are noisy with tons of warnings in code you haven’t even touched or didn’t write yourself.
CodeScene takes a different approach and its quality gates emphasize trends over absolute values; is a hotspot getting better or worse?
CodeScene uses the current state of the code as its baseline during the PR review. This limits the feedback to information that’s relevant and actionable; we never want our code to get worse no matter what level we start at. Trends are actionable.
How does CodeScene calculate a Recommended Review Level?¶
Under the hood, CodeScene calculates a unique risk profile for your codebase based on how the system has evolved and what a typical change set looks like. This risk profile is a combination of technical and social metrics. The technical metrics relate to the depth and diffusion of the change – the more changes and the more widespread, the higher the risk.
The social dimension of the risk profile relates to the experience of the programmer doing the change. The more experienced the programmer, the lower the risk; experience mediates risk. For example, if I make a large sweeping change to the Linux kernel, my change probably has higher risk than an identical change made by Linus Torvalds. Note that experience is relative to a specific repository, and measured as how much each programmer has contributed to your code historically.
Finally, the emphasize is on _prediction_; while it’s likely that a detected high risk change contains a bug, the tool cannot guarantee it, not can it guarantee that lower risk changes are bug free. It’s all about probabilities.
Use a Delta Analysis to Save Time in Code Reviews¶
The main advantage of a delta analysis if that it lets you react to potential problems early. But there’s a potentially large saving at the other end of the spectrum too; Instead of treating all pull requests as equals, CodeScene’s risk classification lets you prioritize your code reviews and focus your time where (and when) it’s likely to be needed the most. Code reviewer fatigue is a real thing, so let’s use our review efforts wisely.
Code review tools like Gerrit lets you select a label. For example, you specify a label that either allows or blocks the change. In addition you may select a label as an opinion (+1 and -1 in Gerrit).
When you integrate CodeScene with Gerrit, it’s our recommendation that you map CodeScene’s risk classification to an automated +1 or -1. For example, all commits below the risk category 3 may be +1, which indicates to the reviewers how much time they need to spend on this review.
Delta analyses lets you auto-detect files that seem to degrade in quality through issues introduced in the current commit or pull request. This is done by calculating code health (see Code Health identifies factors known to impact Maintenance costs and Delivery Risks), which are then supervised for their trend as shown in Fig. 142.
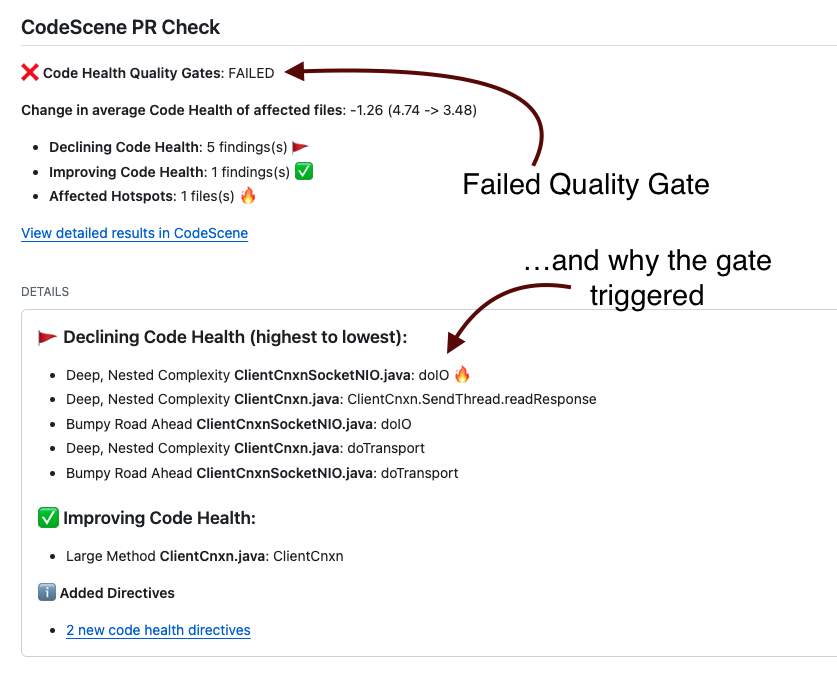
Fig. 142 A Delta Analysis detects degrading Code Health as presented in GitHub Check Run.¶
CodeScene’s delta analysis works in the other direction too; It’s not only about spotting problems. If you enable the quality gates and work pro-actively with Intelligent Notes in CodeScene, then you can allocate less time on the features with 1) low risk, and 2) passing gates, as shown in Fig. 143.
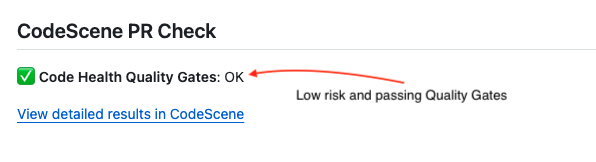
Fig. 143 Spend less time on reviewing code with low risk and passing quality gates.¶
Keep up the Good¶
CodeScene also detects hotspots that improve their code health. This information is included as a positive reinforcement intended to show the effect of the current changeset on the overall code health. Fig. 144 shows an example where a hotspot is successfully refactored – an occasion to celebrate!
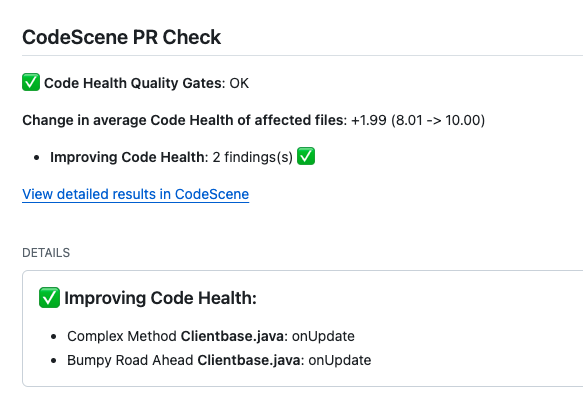
Fig. 144 Measure code improvements as part of the CI/CD pipeline to reinforce a positive trend.¶
Notify the Code Owners on Failed Quality Gates¶
As discussed in Knowledge Distribution, CodeScene parses and includes code ownership information when present. If you have this feature enabled, then CodeScene will include a mention of the code owners should a quality gate fail.